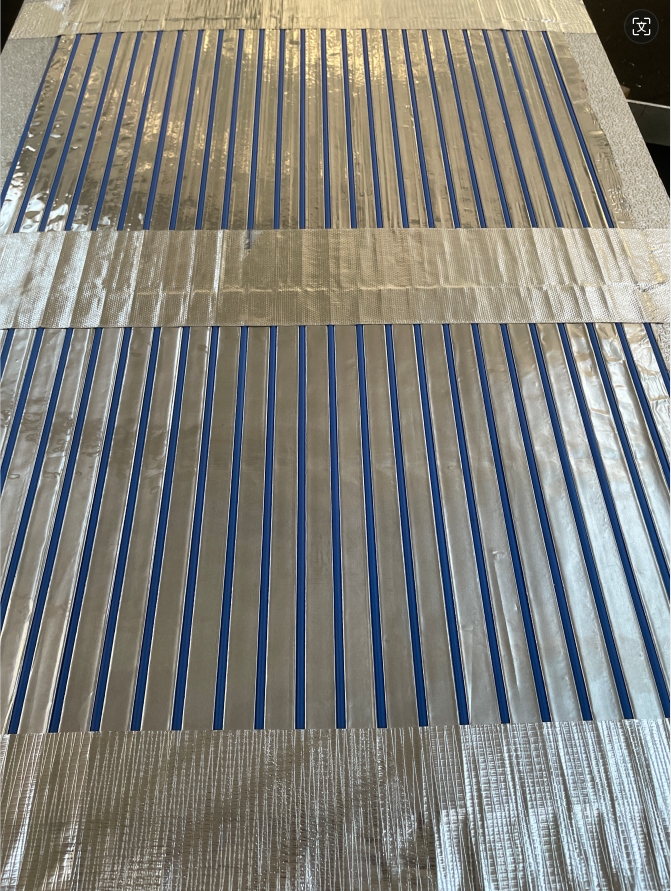
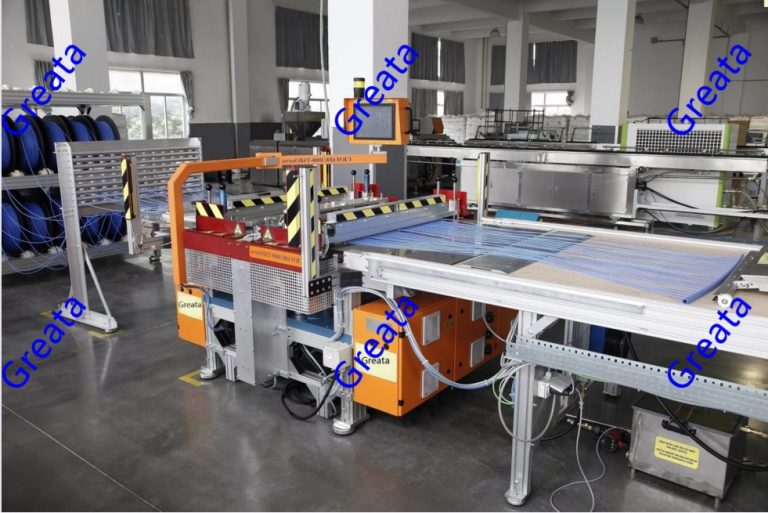
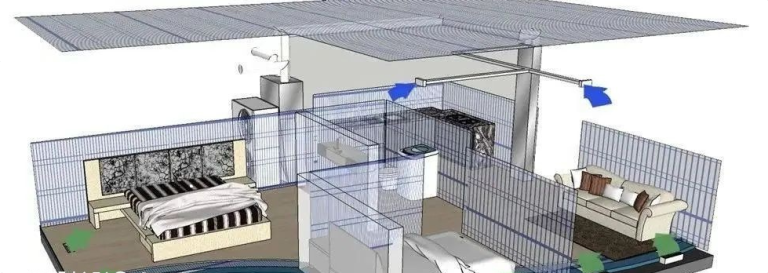
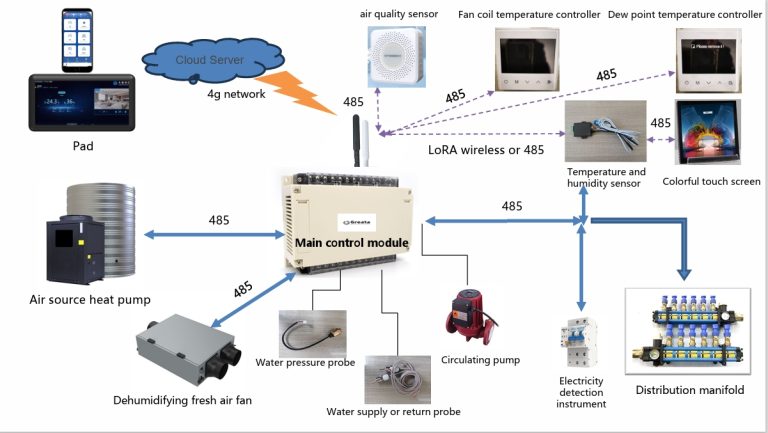
Capillary tube mats for ice storage heat exchange systems are commonly used in buildings for thermal energy storage and air conditioning applications. These mats consist of a network of small-diameter capillary tubes or microtubes that are embedded in a high-conductivity material such as aluminum or copper.
The capillary tubes are usually made of copper and have a diameter between 0.3 to 1.0 millimeters. They are evenly spaced and arranged in a matrix pattern on the mat. The purpose of these capillary tubes is to circulate a heat transfer fluid such as water or a refrigerant.
During the charging phase, the capillary tube mats are filled with chilled water or a refrigerant that has been cooled by an ice storage system. This causes the fluid to flow through the capillary tubes, absorbing heat from the surrounding space and freezing the water in the tubes.
During the discharge phase, when the building requires cooling, the fluid is pumped through the capillary tubes again. This time, the heat from the space is transferred to the chilled fluid, causing the ice in the tubes to melt. The cooled fluid is then returned to the ice storage system for recharging.
Capillary tube mats offer several advantages for ice storage heat exchange systems. They have a large surface area and a high contact efficiency, which enhances the heat transfer process. The capillary tubes also provide a high level of flexibility, allowing the mats to be easily integrated into different building designs.
Additionally, capillary tube mats provide a more uniform temperature distribution across the mat compared to other heat exchange technologies. This helps to improve the overall efficiency and performance of the ice storage system.
In summary, capillary tube mats for ice store heat exchange systems are a reliable and effective solution for thermal energy storage and air conditioning applications in buildings. They provide efficient heat transfer, uniform temperature distribution, and easy integration into different building designs.